The South China Sea reaches a maximum depth of approximately 5,016 meters (16,457 feet). Its average depth is about 1,200 meters (3,937 feet).
The South China Sea, covering an area of around 3. 5 million square kilometers, is a critical maritime region with significant geopolitical and economic importance.
This expansive body of water serves as a gateway to major global sea routes, facilitating immense volumes of international trade.
The rich biodiversity and potential energy reserves in the region have led to complex territorial disputes. Renowned for its vibrant marine ecosystems, the sea supports numerous industries, including fishing and hydrocarbon extraction.
Tourists and researchers are also drawn to its tropical climate and coral reefs, further enhancing its global significance beyond mere depths and distances.
With strategic military interests at play, nations surrounding the South China Sea are keenly invested in the stability and security of the region.

Exploring The South China Sea
The South China Sea, a marginal sea that is part of the Pacific Ocean, spans an approximate area of 3.5 million square kilometers. A rich tapestry of vibrant coral reefs, bustling marine life, and sunken treasures, it is a place of mystery and depth.
Geographical Scope
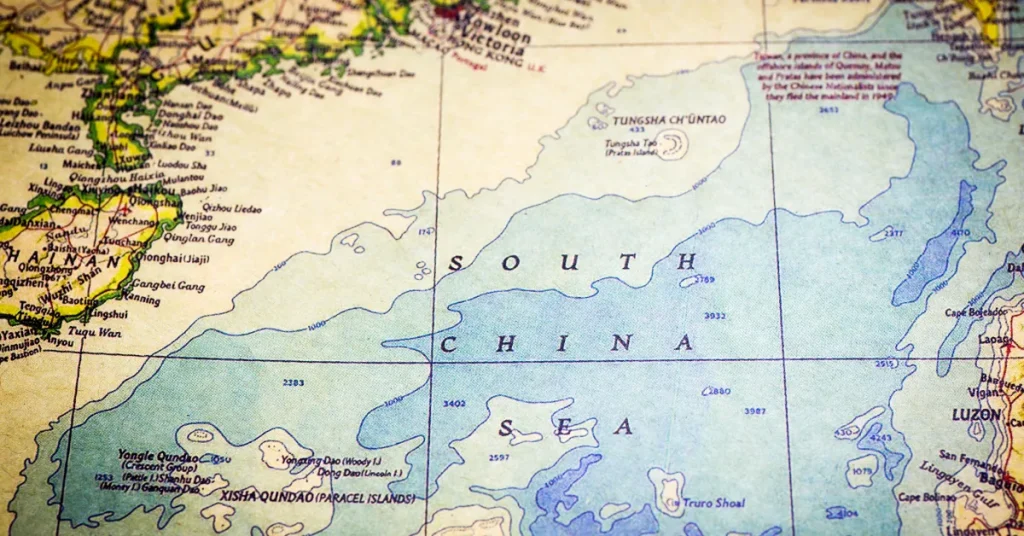
The South China Sea stretches from the Strait of Malacca to the Strait of Taiwan. Surrounded by Asian countries like China, Vietnam, Malaysia, and the Philippines, its waters reach depths that vary significantly.
- Shallowest point: The continental shelf is relatively shallow.
- Deepest point: The China Basin, with depths exceeding 5,000 meters (16,404 feet).
Islands dot the seascape, such as the Spratly and Paracel Islands, some barely above water, others home to military outposts.
At its deepest, the South China Sea challenges the limits of human exploration.
Historical Significance
The South China Sea’s history is as deep as its waters. Centuries of maritime trade have left a legacy of cultural exchange among seafaring civilizations.
| Time Period | Significance |
| Ancient Times | Trade routes for the Silk Road |
| Middle Ages | Navigational advancements |
| Modern Era | Strategic military and trade waterway |
Today, the South China Sea carries one-third of the world’s maritime trade. Its strategic location and natural resources make it a focal point of international interests.
Knowing its depths and historic routes helps us appreciate the sea’s role in shaping human history.
Measuring The Depths Of South China Sea

The South China Sea, a marvel in the Earth’s vast oceans, has depths that have fascinated explorers for centuries.
Knowing how deep this expansive body of water is, provides insights into marine life, navigation safety, and geopolitical significance. Let’s dive into the methods and adventures that reveal the secret depths of this undersea world.
Methods Of Ocean Depth Measurement
Scientists use advanced technology to measure ocean depths. These methods capture the sea’s hidden landscapes far below the waves.
- Echo sounding is a popular technique that involves bouncing sound waves off the sea floor.
- Submersibles enable direct measurement and exploration of ocean depths.
- Satellite altimetry measures the sea surface from space to estimate depth.
Surveys And Expeditions
Surveys map the South China Sea floor, and expeditions seek to understand its deepest points.
| Year | Expedition | Significant Findings |
| 1930s | SS Challenger | First extensive depth recordings |
| 2014 | Li Siguang Hao | Detailed seabed survey |
Such efforts bring the mysteries of the South China Sea closer to the surface for all to see.
Deepest Points And Average Depth
The South China Sea is known for its strategic importance and stunning marine life. Beneath its waves lie secrets about its depth, a topic that fascinates scientists and oceanographers alike.
This body of water harbors areas that are incredibly deep and others less so, contributing to an intriguing maritime landscape.
Challenges Of Deep-sea Mapping
Mapping the ocean’s depths is no easy feat. The South China Sea’s vastness and the difficult underwater terrain present multiple challenges.
Unpredictable weather patterns, deep trenches, and underwater mountains make the process both time-consuming and complicated.
Technology plays a crucial role, yet the ocean’s mysteries often resist easy discovery. Here are some hurdles faced by oceanographers:
- Limited accessibility due to geopolitical tensions
- Rough sea conditions that hinder exploration
- Advanced technology requirements for deep-sea studies
Known Deep Trenches And Basins
Despite these challenges, there are recorded deep points within the South China Sea that spark interest. The most noteworthy feature is perhaps the South China Sea Basin, with incredible depths.
| Feature | Depth |
| China Deep | ~5,000 meters |
| Nansha Trough | ~4,400 meters |
| Manila Trench | ~5,400 meters |
The average depth of the South China Sea is about 1,200 meters. Yet, it is these pronounced trenches and basins that provide key insights into the sea’s true depth. Each holds unique ecosystems and poses incredible opportunities for further research.
Maritime Claims And Strategic Importance
The South China Sea holds extreme global significance with intense international focus on its breadth and depth—both physical and political. This vast expanse, reaching depths exceeding 5,000 meters (16,404 feet), is not just rich in marine resources.
It’s also a strategic military and economic waterway. Here, nations vie for control, asserting maritime claims with significant strategic importance.
Territorial Disputes Over Ocean Depth
Debates regarding ownership of vast underwater territories in the South China Sea are not new. The ocean’s depth is central to these disputes.
Deeper areas can hold untapped resources like oil and gas. Multiple countries claim parts of this sea, based on historical maps or international law.
This struggle for dominance stems partly from the desire to exploit these resources. Nations like China, the Philippines, and Vietnam draw boundaries that often overlap, leading to political friction.
Economic And Military Implications
The economic stakes are high in the South China Sea. A third of the world’s shipping passes through its waters. This sea is rich in fish and hydrocarbons. Nations build naval bases and airfields on small islands to strengthen their claims.
Control over these waters means not just resource access but also military advantage. Countries establish trade routes and security perimeters in this maritime crossroad.
Environmental And Ecological Concerns
The South China Sea, a critical part of the marine ecosystem, is facing several environmental threats. This vast body of water plays a pivotal role in the conservation of marine life.
Its depth influences species distribution and ecosystem health. Let’s delve into the depth’s impact and ongoing conservation efforts in this region.
Impact Of Depth On Marine Life
The varied depth of the South China Sea, reaching as deep as 5,000 meters in places, creates unique habitats. Sunlight cannot reach the deep sea. This fact shapes the types of marine creatures one can find. Here are the key impacts:
- Different species at different layers: As the depth changes, so does the marine life.
- Low light survival adaptations: Creatures adapt to survive in darkness.
- Unique food chains: Depend on resources other than sunlight.
Conservation Efforts In Deep-sea Areas
Conservation initiatives are critical for the South China Sea. They help safeguard its depths and biodiversity. Efforts include:
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs): Areas with restrictions to protect species.
- Regulations on overfishing: To ensure sustainable fish populations.
- Research and monitoring: Providing data to inform conservation strategies.
- International collaboration: Countries around the sea work together.
| Effort | Action |
| MPAs | Implementation of no-take zones |
| Regulations | Enforcing fishing quotas |
| Research | Continuous ecosystem assessments |
| Collaboration | Joint conservation projects |
Protecting the South China Sea is a global responsibility. The future of its deep-sea ecosystems depends on effective management and protection. These efforts will help preserve the sea for generations to come.
FAQs About How Deep Is South China Sea
What Is The Maximum Depth Of The South China Sea?
The South China Sea reaches its maximum depth at the China Deep, registering an impressive 5,559 meters (18,238 feet). This deep trench offers vital insights into marine biodiversity and geological structures.
How Deep Is The Average Depth Of The South China Sea?
On average, the South China Sea has a depth of about 1,200 meters (3,937 feet). This average depth takes into account the various shallows and deeper trenches that make up the sea’s complex underwater terrain.
Why Is The South China Sea’s Depth Important?
The depth of the South China Sea is crucial for several reasons, including strategic naval movements, rich fishing grounds, and diverse ecosystems. Its depth also affects regional climate and underwater resource exploitation.
Does Depth Affect Climate In The South China Sea Region?
Yes, the depth of the South China Sea influences regional climate patterns by affecting ocean currents and water temperature. These, in turn, can impact weather systems, monsoon cycles, and marine habitats.
Conclusion
Exploring the depths of the South China Sea reveals a world of marine mysteries and geopolitical significance. This vast expanse, averaging about 1,212 meters deep, invites further study and respectful navigation.
As we’ve journeyed through its waters together, remember its rich biodiversity and the vital role it plays in global trade.
Sail on with curiosity, respecting the depths that hold centuries of secrets beneath the waves.
Resources:
1. https://www.state.gov/on-the-situation-in-the-south-china-sea/
